구강진료와 생체반응
차례
치과는 무섭다
치과는 무섭다 (67가지 이유)
The extent and nature of dental fear and phobia in Australia
Can you read my pokerface? A study on sex differences in dentophobia
Prevalence of dental fear and phobia relative to other fear and phobia subtypes
Stress
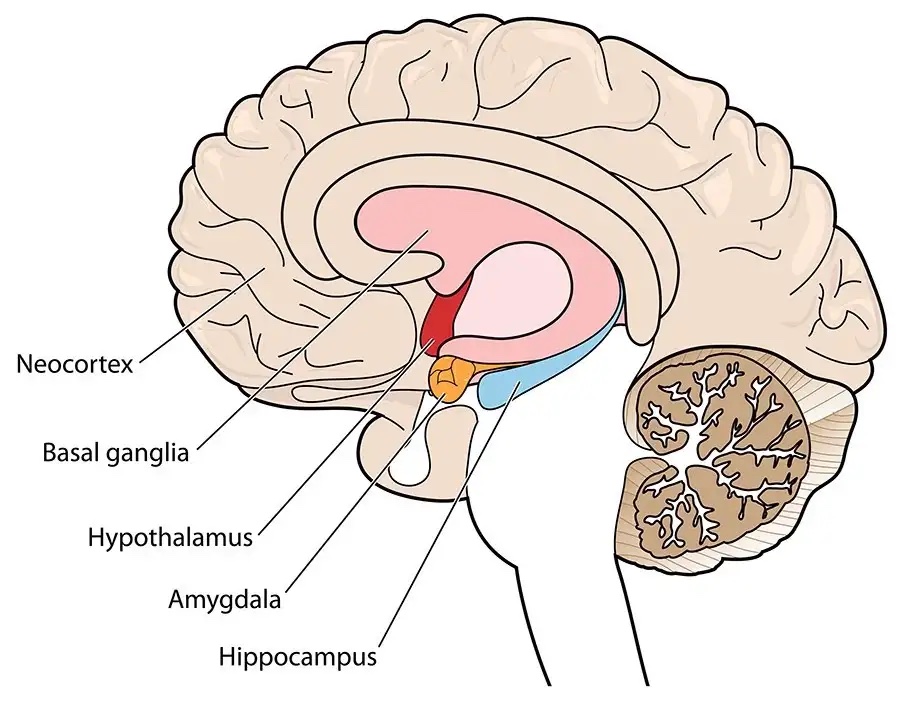
- Amygdala
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical (HPA) axis
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Fight or Flight
Amygdala
HPA axis

실제 and/or 상상의 physical and social 위험 ➔ Amygdala 자극
Amygdala ➔ Hypothalamus의 Paraventricular nucleus (PVN)
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) 유리
Vasopressin (AVP) 합성
전엽: CRH에 반응해서 Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) 합성 + 유리
후엽: Vasopressin (AVP) 유리
Adrenal cortex: ACTH에 반응해서 Glucocorticoid (Cortisol) 유리
시상하부(Hypothalamus)
- 자율신경계 총괄 센터
Limbic system (the medial prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus and the amygdala)에 의해서 조절
excited by the amygdala
inhibited by the hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex
- 위험을 인지하면 교감신경계를 활성화시켜 Fight or Flight 대응을 준비한다.
- 위기가 지나가면 부교감신경계를 활성화시킨다.
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
분비: 시상하부의 PVN中 Magnocellular neurosecretory cell에서 합성 & 유리
분비조절: Oxytocin과 Suprachiasmatic nucleus에 의해 분비량 조절
기능: 뇌하수체 전엽에서 ACTH 합성 및 분비 촉진
Vasopressin (AVP) 합성: 시상하부의 PVN中 Magnocellular neurosecretory cell에서 합성되어 뇌하수체 후엽으로 이동
뇌하수체(Pituitary Gland)
전엽(Anterior)
CRH에 반응해서 Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) 분비
Adrenal cortex에서 Glucocorticoid (Cortisol) 분비 촉진
- 지방세포에서 lipolysis 촉진
- 당뇨병 유발 효과
- 혈액 내 반감기는 4~18분
후엽(Posterior)
Vasopressin: 시상하부에서 합성되어 뇌하수체 후엽으로 이동 후 유리됨
- 신장에서 수분재흡수 증가 ➔ 혈압 높아짐
- 소동맥 수축 (vasoconstriction) ➔ 혈압 높아짐
- 동의어: antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP), argipressin
부신(Adrenal Gland)
- Adrenal cortex
Glucocorticoid (Cortisol) 분비
- Adrenal medulla ➔ Epinephrine + norepinephrine
.svg/450px-HPA-axis_-_anterior_view_(with_text).svg.png)
Cortisol: Stress Hormone
Adrenal cortex의 Zona fasciculata에서 Cytochrome P450에 의해 합성 (전구체: Cholesterol)
- 혈당 조절 기능
저혈당시 Glycogenolysis 유도 ➔ 혈당 높임 (이른 아침에 최고치)
장기간 금식시 간에서 Gluconeogenesis 촉진 ➔ 장기적인 혈당높임효과
- 면역기능 감소
- Interleukin에 의한 T-cell 활성화 억제
- Histamine 분비 억제 ➔ 염증 감소
소장에서 Na+ 흡수 촉진, K+ 배출 증가 (pH 조절 도움)
- 기억력 감퇴
- Hippocampus에 Cortisol receptor 많음 ➔ 장기간의 과다 Cortisol 농도는 Hippocampus Atrophy 유발 (reversible)
참고: 장기간에 걸친 cortisol level 이상
장기간에 걸친 Cortisol 과다: Cushing's syndrome
장기간에 걸친 Cortisol 부족: Addison's disease
|
Addison's |
Cushing's |
||
B.P. |
低 |
Low |
高 |
High |
Ca2+ |
高 |
Hyper-Calcemia |
低 |
Hypo-Calcemia |
Glucose |
低 |
Hypo-Glycemia |
高 |
Hyper-Glycemia |
K+ |
高 |
Hyper-Kalemia |
低 |
Hypo-Kalemia |
Na+ |
低 |
Hypo-Natremia |
高 |
Hyper-Natremia |
스트레스의 증상
혈압상승
- 혈압상승을 유발하는 요인
- 통증
- 얕은 마취나 진정
- 고탄산혈증(hypercarbia)
- 저산소증
- 각성 섬망(emergence delirium)
- 수액 과다 공급(overhydration)
- 고열
부정맥
- 정상인에게서도 스트레스 시 일시적인 부정맥이 관찰된다.
Ryder W.의 연구 (1970)에서, 조사 대상의 29%에서 국소마취 후 치과진료시 심부정맥을 관찰
- 결절성(nodal) 혹은 심방성(atrial) type으로 관찰됨
- 정확한 원인은 모름
실신(Syncope)
- 치과진료시 응급상황의 53%가 실신
- 발생 순서
- 치과, 바늘, 소리 등 스트레스 ➔ 교감신경계 활성 증가 ➔ 혈액이 사지 골격근으로 이동 (fight or flight response)
- 그런데 현실은 진료의자에서 꼼짝 않고 누워 있음 ➔ 정맥환류량 감소, 뇌혈류량도 감소
- 경미한 뇌혈류량 감소 ➔ 창백한 얼굴, 정신 아찔, 시야 좁아짐(Tunnel vision), 오심, 발한, 식은땀, 하품, 동공 확장, 기분 나쁨, 빈맥(보상작용)
부교감신경의 과도한 개입 ➔ 심박수 20회 가량의 심각한 서맥 ➔ 뇌 혈류량 감소 ➔ 실신
- 치과, 바늘, 소리 등 스트레스 ➔ 교감신경계 활성 증가 ➔ 혈액이 사지 골격근으로 이동 (fight or flight response)
- 처치: 누운 자세로 다리 높히면 1분 이내 의식 돌아옴. 특별한 조치는 필요 없음.
- 유발 요인
- 오래 서 있기
- 일사병
- 피 보기(피 뽑기)
- 공포, 불안, 통증
- 탈수
- 발생 순서
- 스트레스, 정신적 불안, 흥분, 긴장이 원인이 되어 발작적으로 과도한 호흡을 하게 됨
과호흡 ➔ CO2 과다 배출 ➔ 동맥혈 CO2 분압이 정상 범위(37~43mmHg) 아래로 떨어짐
- 증상(호흡성 알칼리증): 호흡곤란, 어지럼증, 팔 다리 감각 이상, 경련, 근력저하, 마비되는 느낌, 흉통, 실신
처치: 봉투에 의한 재호흡법(호기 CO2 재흡기)
스트레스시 증가하는 것
- Mental(Brain) activity
- Epinephrine, norepinephrine and cortisol 분비
- 심박수(Heart rate)
- 심박출량(Cardiac output)
- 혈압(Blood pressure)
- 호흡수(Breathing rate)
- 기도 확장(Breathing airways dilate)
- 대사율(Metabolism)
- 산소소비량(Oxygen consumption)
- 뇌 산소 요구량(Oxygen to the brain)
- 골격근 혈류(Blood in muscles and limbs)
- 근수축, 근수축 강도(Muscle contraction, strength)
- 혈액응고기능(Blood coagulation (blood clotting ability)
- 유리지방산(Circulation of free fatty acids)
- 혈중 콜레스테롤(Blood cholesterol)
- Blood sugar released by the liver (근육에 에너지 공급)
- 엔돌핀(Endorphins) from the pituitary gland
- 동공확대(Pupils of the eyes)
- 털이 선다(Hair stands on its end)
- 신장에서 수분 재흡수 증가 ➔ 혈액량 증가(농도 감소) ➔ 혈압증가
- 땀
- Apocrine glands 활동 (체취증가)
스트레스시 감소하는 것
- 면역계 기능
- 골격근 제외 타 부위 혈관 직경, 혈류
- 생식계 기능
- 소화기계 기능
- 침 분비
- 통각
- 내장/방광 괄약근 수축
기도폐쇄
- 진정치료나 전신마취 시 혀의 변위
- 치과이나 치아 등 이물질
- 구토
부록
치대생의 스트레스
스트레스 극복하는 법
TED: 스트레스를 친구로 만드는 법 (Kelly McGonigal)
TED: 스트레스를 받았을 때 침착하게 대응하는 방법 (Daniel Levitin)
TED: The psychology of evil (Philip Zimbardo)
참고자료
Neural regulation of endocrine and autonomic stress responses (Nature Reviews Neuroscience 10: 397–409, 2009)
Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation: Central Role of the Brain (Physiol Rev 87: 873–904, 2007)
The Physiology of Stress: Cortisol and the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
Sex Differences in the Responses of the Human Amygdala (Neuroscientist. 11:288-93, 2005)
부신기능저하증의 진단과 치료 (Hanyang Med Rev 32:203-212, 2012)



.svg/560px-Cushing's_syndrome_(vector_image).svg.png)

